InputFile数据结构分析—ffmpeg.c源码分析
作者:罗上文,微信:Loken1,公众号:FFmpeg弦外之音
struct InputFile 是单个输入文件的管理器。之前在 parse_optgroup() 处理好的 OptionsContext o 变量,有一部分字段会赋值给 InputFile 管理器,如下:
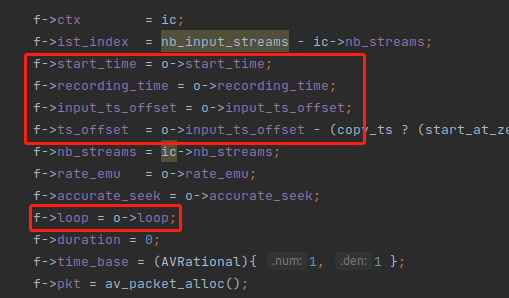
OptionsContext o 变量的另一部分字段,会在 open_input_file() 里面传递给 API 函数,例如:avformat_open_input(),或者赋值给 InputStream 的一些字段。
input_files 全局变量是一个数组,里面的成员正是 InputFile,所以你在二次开发 ffmpeg.exe 的时候,可以通过 input_files 全局变量获取到所有的输入文件的信息。
InputFile **input_files = NULL;
int nb_input_files = 0;
我们接下来仔细学习一下 struct InputFile 的结构,如下:
typedef struct InputFile {
AVFormatContext *ctx;
int eof_reached; /* true if eof reached */
int eagain; /* true if last read attempt returned EAGAIN */
int ist_index; /* index of first stream in input_streams */
int loop; /* set number of times input stream should be looped */
int64_t duration; /* actual duration of the longest stream in a file
at the moment when looping happens */
AVRational time_base; /* time base of the duration */
int64_t input_ts_offset;
int64_t ts_offset;
int64_t last_ts;
int64_t start_time; /* user-specified start time in AV_TIME_BASE or AV_NOPTS_VALUE */
int seek_timestamp;
int64_t recording_time;
int nb_streams; /* number of stream that ffmpeg is aware of; may be different
from ctx.nb_streams if new streams appear during av_read_frame() */
int nb_streams_warn; /* number of streams that the user was warned of */
int rate_emu;
int accurate_seek;
AVPacket *pkt;
...省略多线程结构...
} InputFile;
InputFile 最后的几个字段是多线程用的,ffmpeg.exe 可以使用多线程同时从多个输入文件读取 AVPacket ,然后放到队列里面等待被读取,推荐阅读《ffmpeg多线程读取输入文件》。
在初学 ffmpeg.exe 的时候,为了使代码逻辑简洁,建议把多线程关掉,可以在 configure 的时候通过以下选项关闭。
--disable-pthreads disable pthreads [autodetect]
--disable-w32threads disable Win32 threads [autodetect]
--disable-os2threads disable OS/2 threads [autodetect]
struct InputFile 的各个字段的解析如下:
1,AVFormatContext *ctx,容器上下文,也叫容器实例。
2,int eof_reached,代表输入文件是否已经读取结束。不一定是读到文件结尾才是读取结束。命令行参数也可以用 -t 选项指定输入文件的时长,指定只读取,只处理这么长时间的内容。
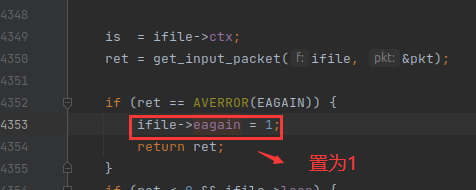
3,int eagain,代表上一次 av_read_frame() 函数是否返回了 EAGAIN 错误码。当 av_read_frame() 函数返回 EAGAIN ,OutputStream 的 unavailable 字段就会置为 1, unavailable 字段代表输出流暂时不可用,只是暂停。如下:
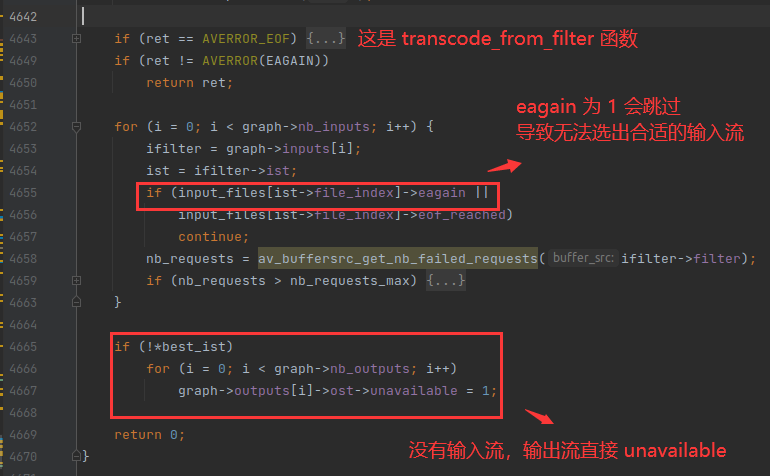
choose_output() 函数的作用是选出最小时间的输出流,例如音频流已经输出了2分钟了,视频流才输出1分钟,choose_output() 函数就会返回 视频流。
但是如果视频流 (OutputStream) 的 unavailable 字段为 1,choose_output() 函数就不会返回视频流,而是返回 0 。
从而会导致进入休眠的逻辑,如下:

上图中的 reset_eagain() 函数会重置 eagain 跟 unavailable 字段为 0 ,所以休眠之后可以继续运行了。
这个逻辑的流转比较复杂,建议读者自行调试一番,这里提前讲了一些知识,所以有个印象就行。
简单来说,就是如果 当 av_read_frame() 函数返回 EAGAIN,就会休眠一段时间再读取,你在调 ffmpeg API 函数的时候也可以效仿这种做法。
4,int ist_index,输入文件的第一个流在 input_streams[] 数组的位置索引。
input_streams 是一个全局变量数组,存放所有的输入文件的所有的输入流。
5,int loop,此输入文件应该被循环读取多少次。例如下面的命令:
ffmpeg -stream_loop 2 -i juren.mp4 juren.flv
最后生成的 juren.flv 会比 juren.mp4 的时长大一倍。实际上就是两部 mp4 拼接起来。
6,int64_t duration,在循环读取的时候用的,开始第二次循环之前,会把 duration 设置为流的时长,第二次循环的时候 pts 会加上 duration,这样时间就拼在一起了,如下:
duration = av_rescale_q(ifile->duration, ifile->time_base, ist->st->time_base);
if (pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
pkt->pts += duration; //加上之前的时长,
...省略...
}
7,AVRational time_base,duration 字段的时间基。
8,int64_t input_ts_offset,直接把命令行选项的 -itsoffset 5 赋值过来的,会设置成 5 ,只在一个地方被用到。
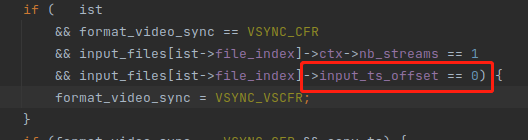
9,int64_t ts_offset,input_ts_offset 跟 ts_offset 的应用逻辑非常复杂,初学者不需要关注这两个变量,默认这两个变量是 0 ,推荐后面阅读《xxxx》
10,int64_t last_ts,记录的是最近一次读取出来的 AVPacket 的 dts 时间。
11,int64_t start_time, 命令行的 -ss 选项赋值过来的参数,代表从输入文件的 第 N 秒开始处理。时间基是 AV_TIME_BASE
-ss 选项是通过 trim 滤镜实现的,trim 滤镜可以指定从那个时间点开始裁剪。
12,int seek_timestamp,这个字段没有使用的,应该是他想记录一下 seek 的时间,但是实际没有记录。
13,int64_t recording_time,输入文件的最大处理时长,例如一个文件3分钟,可以通过命令行选项 -t 60 指定只处理 1分钟的时长。限制时长是通过 trim 滤镜实现的。
14,int nb_streams,输入文件实际的流数量,可能会比 ctx.nb_streams 大,因为有些文件,可能 av_read_frame() 会读出其他流,应该是 ctx.nb_streams 记录的大小不准确。
15,nb_streams_warn,等于 nb_streams 减去 ctx.nb_streams ,实际上就是动态读取到的流数量。
16,int rate_emu,命令行参数 -re 赋值过来的,代表按照帧率去输出,可以模拟现场直播。
17,int accurate_seek,
enable/disable accurate seeking with -ss
18,AVPacket *pkt,从 av_read_frame() 里面读取出来的 AVPacket。
